About CBGP
Among these, arthropods that attack or transmit infectious agents to crops, invasive alien species, reservoirs of zoonoses and their vectors, are the focus of increasing attention.
CBGP approaches the issue of population management of these animal species using the principles of integrative systematics, ecology and evolutionary sciences. The aim of the research carried out here is to characterise patterns of diversity at multiple scales (from gene networks to species communities) and to understand the ecological and evolutionary determinants, in order to gain a better understanding of the evolution of these complex biological systems and to help improve their control.
CBGP is positioned at the interface between academic research and applied research: our unit is known as a centre of excellence in systematics, phylogeny, phylogenomics, population genetics and genomics, interaction ecology and health ecology, as well as for the quality of its expertise in the management of health crises linked to plant health, the consequences of bio-invasions and zoonotic risks.

Research conducted at CBGP is part of the many threats, amplified by a context of global change, that currently affect food security, biodiversity and health.
CBGP members are involved in higher education at the Institut Agro Montpellier, the University of Montpellier and many other universities in the North and South.
Beyond its primary research and training mission, CBGP is involved in awareness raising, extension and scientific mediation with the general public (novice or interested) on issues related to pest management, biological invasions, health ecology, agroecology and biodiversity conservation.
CBGP has a long-standing and privileged partnership with many institutions in the South.
Research conducted at CBGP is part of the many threats, amplified by a context of global change, that currently affect food security, biodiversity and health.
CBGP members are involved in higher education at the Institut Agro Montpellier, the University of Montpellier and many other universities in the North and South.
Beyond its primary research and training mission, CBGP is involved in awareness raising, extension and scientific mediation with the general public (novice or interested) on issues related to pest management, biological invasions, health ecology, agroecology and biodiversity conservation.
CBGP has a long-standing and privileged partnership with many institutions in the South.
We are working to ensure that there is gender parity in all the UMR’s decision-making bodies (management, extended management college) and consultative bodies (CU, CS, etc.).
The current W/M ratio is 0.6 for all staff, but it reverses (1.3) for the subset of staff in positions of responsibility (members of the Executive Committee) and tends towards 0.7 if we include staff in cross-functional positions. More generally, we are counting on everyone becoming aware of the gender issues involved in ensuring that women are fairly represented in scientific life. The Executive Committee has appointed two gender equality officers.
33/54
W/M ratio in the unit
12/17
Ratio W/M in positions of responsibility and cross-functional functions
We are attentive to the quality of working life, and encourage the establishment of a collaborative environment and relationships of trust between employees.
In order to maintain a pleasant social life in the unit, the organisation of recreational events is encouraged and supported (Christmas meal, galette des rois, barbecue, etc.), as are leisure activities on the site (bee-keeping club, for example).
CBGP is committed to a proactive policy to reduce the energy and ecological footprint of our activities.
In particular, we will be concentrating our efforts on replacing energy-guzzling lighting (fluorescent tubes, compact fluorescent bulbs) with light-emitting diode (LED) lighting, controlling our electricity consumption, managing plastics and waste, and preserving biodiversity on our site. Lastly, CBGP has drawn up a greenhouse gas emissions balance sheet, as part of a sustainable development approach that takes into account the environmental impact of its activities.
567 tCO2e
GHG emissions
CBGP is attached to the scientific departments SPE and ECODIV of INRAE, BIOS of CIRAD, ECOBIO of IRD, and BE of the Institut Agro Montpellier. It participates in many local and national structures: the CeMEB and AGRO LabEx, the agronomy-environment-biodiversity cluster of the MUSE I-site, the key challenges Occitanie Region BiodivOC and RIVOC, the Vectopole South network, the RARe research infrastructure, …
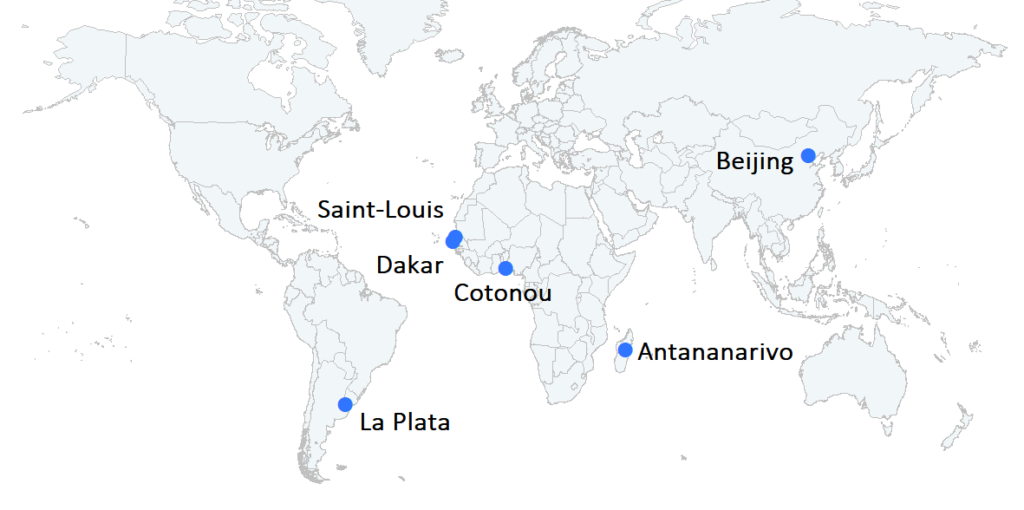
CBGP collaborates with colleagues and institutions in many countries, and participates in several international programs (BIOPOLIS, LIA IFOPE, IRN WAN@BI, IRN RESET GGW, …). The international projection of CBGP involves many field missions and with partners, as well as expatriations (West Africa, Madagascar,…).
La Plata, Argentina |
ECOS Sud cooperation |
|
Dakar, Senegal |
BIOPASS Lab |
|
Saint-Louis, Senegal |
BM UFR S2ATA Lab |
|
Cotonou, Benin |
Epidemiological surveillance Port platform |
|
Antananarivo, Madagascar |
Institut Pasteur |
Expatriation of Gauthier Dobigny |
Beijing, China |
Beijing Forestry University |
LIA IFOPE : Invasive FOrest Pests in Eurasia |